Page 92 - CMA Journal (Nov-Dec 2025)
P. 92
S B
• Transparency Through Green Taxonomy: Implementing national and international climate goals, such as UN SDG
the Green Taxonomy and standardized disclosures will 13: Climate Action, ISO 14001, IFRS S2, and GRI standards.
improve transparency, strengthen data integrity, and align Structured ESG assurance processes including carbon
Pakistan with global green finance benchmarks. Banks must footprint verification, emissions validation, and
institutionalize climate disclosures and strengthen risk climate-related disclosures ensure credibility and investor
analytics to enhance portfolio resilience and investor trust. confidence.
• Digital Finance for Inclusion: Digital Financial Services • Emerging Frameworks Integration: Harmonizing with
can enhance financial inclusion while reducing frameworks such as the ISSB and embedding TCFD
operational carbon footprints. Fintech solutions can recommendations strengthens transparency and
expand access to green finance for underserved facilitates decision-useful reporting. Banks can integrate
communities and regions. TCFD-aligned reporting at Board and Executive levels to
support sustainable investment and long-term value
• Climate in Accounting and Audit: Accounting, Audit, and
Assurance functions should embed climate considerations creation.
into planning, execution, reporting, and governance • Long-term Green Financing: Beyond 2030, banks must
oversight. Banks must provide mandatory role-specific fully embed climate risk into strategic, operational, and
training for auditors and monitor climate risk exposures, investment frameworks. They are expected to finance
especially in carbon-intensive sectors such as textiles, low-carbon projects, support climate adaptation, mobilize
cement, and construction. private capital for sustainable development, and innovate
financial products to build a resilient, net-zero-aligned
• Global Standards Alignment: Banks and organizations
must align governance, reporting, and operations with economy in Pakistan.
a
egic
k
a
t
Gr
vie
v
er
of
w
w
w of Gr
O
S.W
e
ing in P
een Bank
T
.
.
O
stan
i
Str
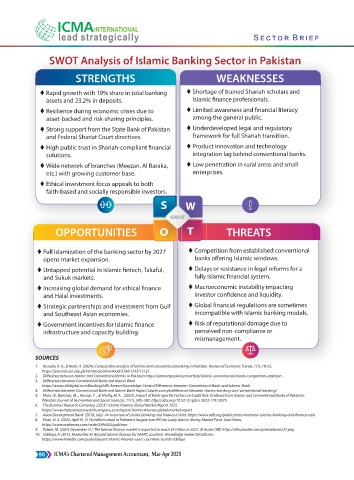
Strategic S.W.O.T Overview of Green Banking in Pakistan
The following provides a brief overview of Green Banking in Pakistan using the S.W.O.T framework and does not represent a detailed analysis
STRENGTHS WEAKNESSES
Promotes NDC targets, aligns with SDGs, enhances brand Underdeveloped domestic green capital market and
Un
reputation among environmentally conscious stakeholders.
limited investor awareness in equity markets.
li
m
Engagement with international organizations (IFC, World Gr
Green finance constitutes a small fraction of total lending,
Bank, UNDP, COP) attracts foreign investment with building w
with exposure concentrated in climate-sensitive sectors.
technical capacity of local banks.
In
Inconsistent enforcement of green banking guidelines
Potential to scale green lending and finance renewable across local banks reduces uniform adoption, financial
ac
energy, climate-smart agriculture, resilient housing, and SME effi
efficiency and effectiveness.
adaptation projects, leveraging Pakistan’s solar, wind, and
Macroeconomic constraints, including inflation and
hydro resources. M
currency volatility, increases the cost of green financing
cu
Operational and financial advantages include reduced costs an
and limit its scope and scale.
(paperless banking, solar-powered branches, energy
efficiency), improved profitability, and strengthened risk
risk
k
management through ESG integration.
S W
SWOT
OPPORTUNITIES O T THREATS
OPPORTUNITIES
t
r
Strengthen transparency, ESG integration, and investor Po li cy y u n
o
r
Policy uncertainty, inconsistent regulatory enforcement,
es,
confidence by implementing standardized disclosures, political
political instability, and macro-financial pressures including
climate risk reporting, and adherence to frameworks such as interest rate hikes, fiscal deficits, and currency volatility
as
IFRS-S2, UN SDGs, and Pakistan Green Taxonomy promises undermining market confidence and increasing costs for
smooth transition to net-zero-aligned economy of Pakistan. n. green projects.
Scaling up climate finance to meet Pakistan’s projected Socio-economic, cultural, and regulatory barriers, limited
USD 340 billion demand by 2030 across renewable energy, public-private coordination, transition risks, and high
climate-resilient infrastructure, climate-smart agriculture, compliance costs hindering the adoption and scaling of
and SME adaptation projects will create more green jobs. green banking practices.
by
Enhancing operational resilience and institutional capacity by Weak investor confidence and risk of greenwashing in green
embedding ESG risk management, technical training, and bonds, sukuks, and other climate-linked financial products if
capacity-building programs across the banking sector will ESG initiatives are implemented superficially or without
increase the local banks technical skills. measurable impact.
Establishing green banking as a strategic competitive High exposure to climate and environmental risks such as
advantage by creating a niche market and enhancing floods, heatwaves, glacial lake outbursts, and air pollution
long-term climate risk management position Pakistan as affecting borrowers, assets, and financial stability,
strong regional player. compounded by rising non-performing loans in
climate-sensitive sectors.
2
02
d
ere
M
emen
g
ana
t
s
’
CMA
ar
h
C
t
D
-
ov
D
c
e
N
ccoun
A
t
,
t
an
900 I ICMA’s Chartered Management Accountant, Nov-Dec 20255
9